HISTORY OF YOGA
The Vedas were a collection of science of Mother Nature, agriculture, mathematics, astronomy, social sciences, ethics & morality, culture, arts, Ayurveda, and much more.

PRE-CLASSICAL YOGA
VEDAS - 10,000 BC - 500 BC

The yoga science was first mentioned in the vedas, which date back more than 10,000 years. The earliest Vedic text discovered dates back about 7,500 years. The Vedas are thought to have been passed down orally for at least twice that long.
The Vedas contained a wealth of information on a wide variety of topics, including agriculture, mathematics, astronomy, sociology, ethics, art, culture, and Ayurveda, to name a few. During that historical period, religious chants, mantras, and rituals were produced and taught as part of the Vedas. The four divisions of the Vedas are called Aranyaka, Samhita, Brahman, and Upanishads. The earliest references to yoga can be found in the Upanishads. The primary goals of Upanishads are the withdrawal of the senses, the mastery of the intellect, and the achievement of nirvana.
The four major Vedic texts are the Rigveda, Samaveda, Yajurveda, and Atharvaveda.
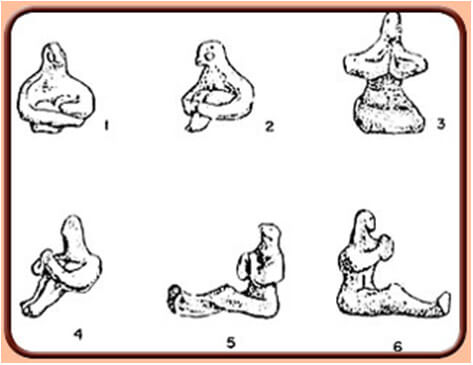
Artefacts from the Past
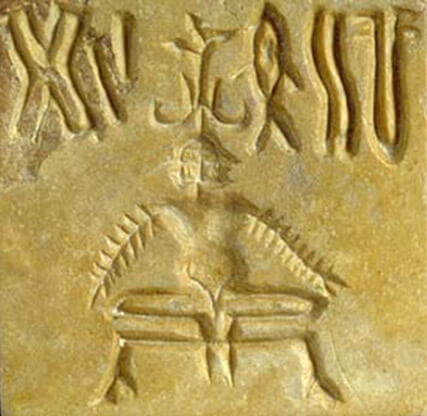

Over five thousand years ago, in the time of the Aryan culture of the Indus Valley, the first tangible evidence of yoga emerged. Numerous seals of a seated human figure, apparently in meditation, were discovered during archaeological digs in the area.
RAMAYANA
The historical account of Lord Rama, which dates back over 7,000 years, is a vital part of Yoga philosophy and practise. The Ramayana is a 24,000-verse epic poem that recounts the tragic life of King Rama of the kingdom of Ayodhya. King Rama, however, is able to keep his composure and lead a life of virtue despite the challenges he faces.

Everything he does is done to discharge some obligation or responsibility to someone else. Despite leading such a selfless life, he has never been happier. Herein lies the essence of yoga.
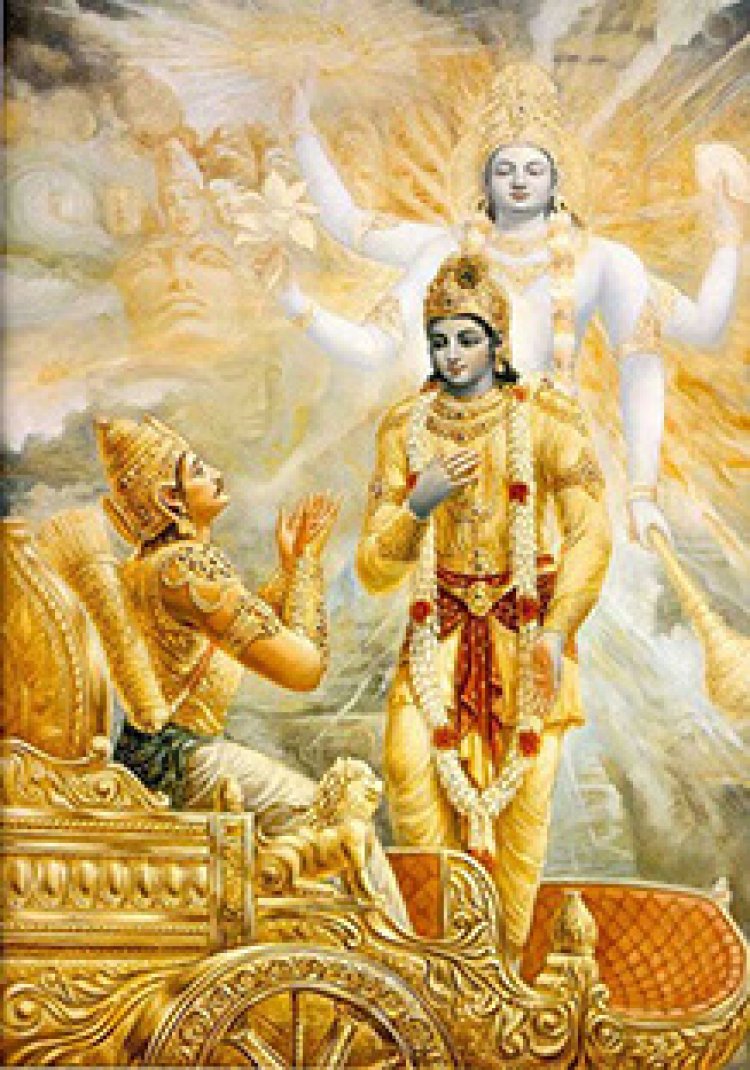
MAHABAHARATA
Mahabharata is another essential historical account for yoga science. Lord Krishna, the most revered Yoga master, lived around five thousand years ago, and here is his story. There are more than 200,000 verse lines in Sage Vyasa's Mahabharata, making it one of the longest epic poems ever written. The Bhagavad Gita, the single most important ancient text on yoga, is included here. Yoga psychology and the science of living are two more names for the Bhagavad Gita. It offers answers to the challenges that people face. The lessons of the Bhagavad Gita have been followed by numerous advanced civilizations across the ages. The Gita has been considered the most priceless of all knowledge by many sages, gurus, and yoga teachers.

The Bhagavad Gita is a conversation between Krishna, a symbol of the highest level of consciousness, and Arjuna, a human being. Prince Arjuna consults with Lord Krishna for advice. Arjuna is feeling down and hopeless about life. Prince Arjuna finds inspiration and motivation from Lord Krishna, who enlightens him to life's meaning and purpose. Dharma, Karma Yoga, Bhakti Yoga, and Jnana Yoga are all discussed by Krishna.
CLASSICAL YOGA – 500 BC
In 500 B.C., the great Sage Patanjali codified yoga practises in a systematic way. He penned the Yoga Sutras to provide a comprehensive description of how to consciously awaken and develop your higher mental capacities. Asanas, Pranayama, Pratyahara, Dharana, Dhyana, and Samadhi were all part of his Ashtanga yoga practise. The Yoga Sutras consist of only 196 Sanskrit lines organised into 4 sections.
POST-CLASSICAL YOGA - 800 AD

A revolutionary Yoga Master named Shankaracharya, who lived around the year 800 AD, revitalised the yoga tradition. He brought together competing schools of yoga, reconciled ideological disagreements, and broadened interest in the science of yoga. Wonderful insights into the science of yoga can be found in his comments on the Bhagavad Gita, the Upanishads, and Vedant philosophy. Swami Sannyasa, or monks, had a significant good influence in society after he established their tradition.
(HATHA YOGA) 600 AD - 1500 AD
The most well-known school of yoga, Hatha, emerged between the years 600 and 1500 AD. Hatha Yoga is a branch of yoga that aims to purify and strengthen the body and the mind. Asanas, cleanses, pranayama, mudras, and bandhas are all used to bring the body and mind into balance. Sages Matsyendranath and Gorakhnath are credited with creating Hatha yoga. This style of yoga was more accessible and beneficial to everyone's health.
MODERN TIMES 1890'S
The most well-known school of yoga, Hatha, emerged between the years 600 and 1500 AD. Hatha Yoga is a branch of yoga that aims to purify and strengthen the body and the mind.
 Asanas, cleanses, pranayama, mudras, and bandhas are all used to bring the body and mind into balance. Sages Matsyendranath and Gorakhnath are credited with creating Hatha yoga. This style of yoga was more accessible and beneficial to everyone's health.
Asanas, cleanses, pranayama, mudras, and bandhas are all used to bring the body and mind into balance. Sages Matsyendranath and Gorakhnath are credited with creating Hatha yoga. This style of yoga was more accessible and beneficial to everyone's health.













